

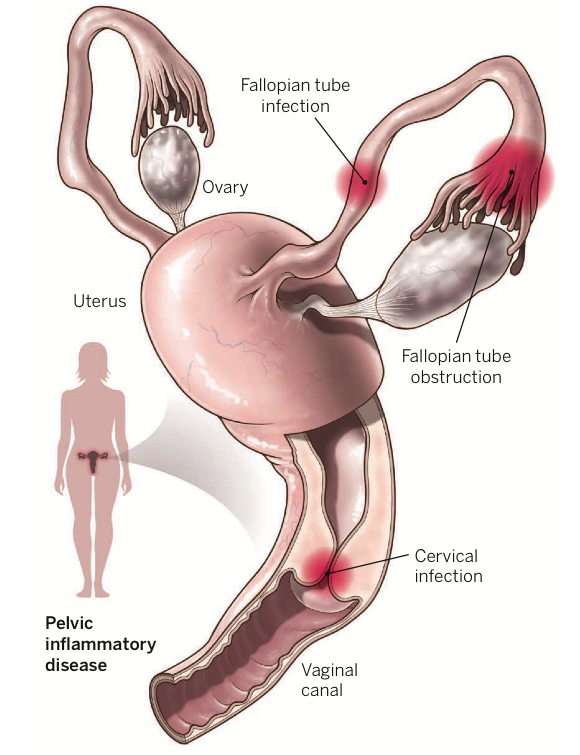
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or PID is an infection of female reproductive organs. This usually happens when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to your uterus, fallopian tubes, or ovaries, causing inflammation in these areas. However, there is no symptom of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. You do not even realize the disease. Often this disease is detected in the woman having trouble getting pregnant or developing chronic pelvic pain. Most cases of this are due to STIs that spread to the vagina or cervix. If this disease is not taken care of in time, PID can cause problems in pregnancy, problems during pregnancy, and prolonged pelvic pain.
Table of Contents
What Is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID?
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or PID is becoming a major cause of infertility in women of metro cities. This problem is more common in girls aged 15-24 years. This can affect their fertility. It is a hormonal disorder in which there is swelling of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and reproductive organs of the patient. In the absence of treatment, there is a possibility of infertility.
According to experts, this disease is more common to women who are of childbearing age and suffer from back pain. In addition, women who have a prior history of the disease often have to go through this problem. So, in today’s article, we are going to give you all the information related to PID. By reading this, you can find out this disease and also treat it as soon as possible.
(Also Read: How Does The Menstruation Cycle Works?)
How Does Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID Happen?
A woman may have PID when bacteria pass from her vagina or cervix to her reproductive organs. Many different types of bacteria cause PID, but PID is often caused by two common STIs, namely Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea, and Chlamydia. In recent years, there has been a decline in the number of women suffering from PID. This is because now more and more women are being tested regularly for gonorrhea and chlamydia. According to experts, you can also have PID without STI. Normal bacteria in the vagina can enter a woman’s reproductive organs and cause PID.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID Symptoms:
Many women do not know for a long time that they are suffering from PID, because they do not show any specific symptoms. Symptoms of PID can be very mild or very severe. Which you need to pay attention to. Below we are telling you about the possible symptoms of the Pelvic Inflammatory Disease so that you can start treatment as soon as possible in time.
- Lower Abdominal Pain
- Fever
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain during sex
- Pain while urinating
- Irregular menstruation
- Upper right abdominal pain
- Bleeding between periods
- Fatigue
- Pain in the lower back and rectum
- Frequent urination
- Vomit
- PID disease can come rapidly with severe pain and fever. Especially if it is caused by gonorrhea.
(Also Read: What Is Your Vaginal Discharge Saying About Your Health?)
What Are The Causes Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID?
PID disease usually starts with an infection, called STI. This infection starts from the vagina and spreads to the cervix. It then grows in the fallopian tube and ovary, causing inflammation in the tube and causing an already small tube to become smaller. Due to this infection, there are lesions in the tube and due to blockage, the fertilizing egg is unable to move properly. The cause of infection can be bacterial, fungal, and parasitic. Which causes PID disease. That is, many bacteria can cause PID. These bacteria usually thrive during unprotected sex. Sexually transmitted bacteria are the most common cause of PID. Chlamydia is the most common, followed by gonorrhea.
According to the American Family Physician, 80–90 percent of women with chlamydia and 10 percent of people with gonorrhea do not show any symptoms.
What Are The Risk Factor Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID:
Apart from STIs, certain risk factors increase the risk of developing PID, which you can learn about here. Bacteria enter the vagina. If the cervix is not completely closed, the infection can spread more easily. Which increases the risk of miscarriage.
- An intrauterine device is a form of birth control that is placed in the uterus. This can increase the risk of infection, leading to PID.
- During an endometrial biopsy, a sample of tissue is taken for analysis. This increases the risk of infection and subsequent PID.
- If the infection spreads from the appendix to the pelvis, appendicitis has a very low risk.
- If you are sexually active under 25 years of age.
- Being in a relationship with a man who has more than one sexual relationship.
- Having sex without a condom.
- If there is a history of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease or sexually transmitted infections in the home.
(Also Read: What Are The Symptoms Of Ovulation? )

What Are The Complication Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID?
If PID is not treated at the right time, many complications may arise. Untreated pelvic inflammatory disease can be the cause of scar tissue. You can also develop a collection of infected fluid (abscess) in your fallopian tube, which can damage your reproductive organs.
Ectopic Pregnancy:
PID is a major cause of tubal (ectopic) pregnancy. In an ectopic pregnancy, scar tissue from PID prevents fertilized eggs from being implanted into the uterus via the fallopian tube. Ectopic pregnancies can cause large-scale, hemorrhagic bleeding and require emergency therapy.
Infertility:
PID can damage your reproductive organs and cause infertility (inability to become pregnant). The more often you have PID, the higher your risk of infertility. Delaying treatment for PID also increases the risk of infertility.
Chronic Pelvic Pain:
Pelvic inflammatory disease can cause pelvic pain that can last for months or years. Scarring in your fallopian tubes and other pelvic organs can cause pain during sexual intercourse and ovulation.
Tube-ovarian Abscess:
PID can be the cause of the accumulation of pus – an abscess in your uterine tube and ovaries. If left untreated, you can develop a life-threatening infection.
The probability of infertility increases by 20 percent due to a fallopian tube of a woman with PID and a 9 percent risk of ectopic pregnancy. While the probability of developing chronic pelvic pain is 18 percent.
(Also Read: Ways To Remove Vaginal Hair At Home)
How Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or Is Diagnosed?
To diagnose PID, doctors usually perform a physical test to check for signs of PID and to test for STIs. If you think you may have PID, contact a doctor as soon as possible. If you have lower abdomen pain, the doctor will test the following things.
- Abnormal discharge from the vagina and cervix
- Is there an abscess near your ovary or fallopian tube?
- Whether you have pain in your reproductive organs
Also, your doctor may perform tests to find out if you have PID or have a different type of problem that looks like PID. These may include-
- Tests for STIs such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. These infections can cause PID.
- You can perform a test for urinary tract infection or other conditions, which can cause pelvic pain.
- An ultrasound scan can be used to check for inflammation in the fallopian tubes. Laparoscopes are also sometimes used to visualize the area.
- During this procedure, your doctor inserts a thin, lighted instrument through a small incision in your abdomen to look at your pelvic organs. Who takes pictures of your pelvic organs.
- The doctor may perform an ultrasound or another imaging test to check the internal organs for signs of PID. Let me tell you that a Pap test is not done to detect PID.
(Also Read: How Many Days Does It Take To Reveal Pregnancy Symptoms)

Treatment For Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID:
Early treatment of PID, treatment for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, reduces the problem of complications. Know below how PID can be treated.
Antibiotic Treatment:
The first treatment of PID is with an antibiotic. It is very important to follow the instructions of doctors. A course usually lasts 14 days and at least two anti-biotic drugs are used together, which work against different bacteria. This includes antibiotics such as Cefoxitin, Metronidazole, Ceftriaxone, and Doxycycline (Metronidazole, Ceftriaxone, and Doxycycline). To see if the antibiotic is working, see the doctor once again after two to three days of taking it. If it does not affect for three days, then further treatment should be started.
Hospitalization:
If a woman with PID is pregnant, she may need to be admitted to the hospital.
Surgery:
By the way, after such treatment, surgery is rarely needed. But if there is a scar (wound) on the fallopian tube or there is an abscess, then surgery may be required. For this, keyhole surgery has to be done.
Treatment For Your Partner:
To prevent reassessment with an STI, your sexual partner or partners should be screened and treated. Because infected partners may not have any noticeable symptoms.
Temporary Abstinence:
Avoid sexual intercourse until the treatment is complete until tests confirm that the infection has gone away from all partners.
(Also Read: Essential Sexual Hygiene Tips For Women After Sex)
What Are The Prevention Of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Or PID?
PID can become a serious condition, but there are some ways to reduce this risk, which you must know.
- Get screened regularly. Especially those with multiple sexual partners.
- Ensuring sexual partners to check for infection and STIs.
- Use a condom during sexual intercourse. Each time you have sex, limit your partner’s number and ask about the potential partner’s sexual history.
- Wash the vagina back and forth on both sides after using the bathroom to prevent bacteria from entering your vagina.
- Do not have sex immediately after childbirth or pregnancy termination.
- Avoid starting sex again until the cervix is closed properly.
- Talk to your doctor about contraception. If you regularly take birth control pills, it is necessary to use condoms every time to prevent STIs.
- If you are at risk of STIs like Chlamydia, contact your doctor for a test. Set the screening schedule if necessary. Early treatment of STIs gives you the best chance of avoiding PID.
- Eat a healthy diet and drink plenty of water.
- Go to the toilet after sex.
- Take great care of cleanliness after periods.
- Do not douche. Douching increases the imbalance of bacteria in your vagina.
- Drink grapefruit juice to avoid PID. It has the properties of destroying bacteria and fungus.
- If you have an STI, then you should advise your partner to get it checked, also get treatment if needed.
Can I Get Pregnant If I Have PID?
If you have had PID more than once, you are very unlikely to become pregnant. When you are battling PID, bacteria can enter the fallopian tubes or cause tube inflammation. This can cause scarring in the tissue, which forms your fallopian tube. This scar can prevent an egg from spreading from your ovary or from the fallopian tube to your uterus. PID can cause scar tissue to cause ectopic pregnancy instead of a normal pregnancy.
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a disease that is curable and in many cases, women recover completely. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1 in 8 women with a history of PID has difficulty getting pregnant. According to experts, this infection can occur again in two years after being cured. However, this happens in one in five cases, so awareness of PID i.e. pelvic inflammatory disease is very important. Talk to your partner about this and keep your regular checkup done.








Leave a Comment